CBSE CLASS 10 BOARD 2024 ALL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS

class6,class7,class8,class9,class10,class11,class12,government jobs news,cbse update news,jobs,competition exams,india news,news update,tech news,health news,mcq questions,question answer in hindi ,question answer in english,short answer type questions,very short answer type questions,product reviews,current affairs update news ,travel blog ,education news ,govt vacancy,competition exams notification,saraswati tuition centre,exam notes,maths concept,reasoning ,exam syllabus,ncert ,practice paper

Question 1.
Who exercises all governmental powers?
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Chief Justice of the Supreme Court
(d) Chief Election Commission
Answer: (b) Prime Minister
Question 2.
The Second Backward Classes Commission was appointed by the government of India in
(a) 1979
(b) 1981
(c) 1985
(d) 1999
Answer: (a) 1979
Question 3.
Which one of the following statement about the President is wrong?
(a) He is the head of the state.
(b) He is the highest formal authority in the country.
(c) He exercises only nominal powers.
(d) He is elected directly by the people.
Answer: (d) He is elected directly by the people.
Question 4.
The strength of the Council of Ministers ranges from
(a) 60 to 80
(b) 60 to 100
(c) 70 to 85
(d) 80 to 100
Answer: (a) 60 to 80
Question 5.
Once the Lok Sabha passes the budget of the government or any other money related law, the Rajya Sabha cannot rejected it. The Rajya Sabha can only delay it by
(a) 14 days
(b) 15 days
(c) 16 days
(d) 17 days
Answer: (a) 14 days
Question 6.
When was the Second Backward Class Commission appointed?
(a) 1989
(b) 1979
(c) 1999
(d) 2001
Answer: (b) 1979
Question 7.
What do the Civil Servants do?
(a) They take important policy decisions
(b) They implement the ministers’ decisions
(c) They settle the disputes
(d) none of the above
Answer: (b) They implement the ministers’ decisions
Question 8.
What is ‘Parliament’?
(a) Assembly of elected representatives at the national level
(b) A body consisting of appointed ministers
(c) Body comprising judges
(d) Assembly of only appointed members
Answer: (a) Assembly of elected representatives at the national level
Question 9.
Apart from Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, who else constitutes the Parliament?
(a) Prime Minister
(b) Chief Minister
(c) Governor
(d) President
Answer: (d) President
Question 10.
For how long can the Rajya Sabha delay a Money Bill?
(a) 15 days
(b) 1 month
(c) 3 months
(d) 14 days
Answer: (d) 14 days
Question 11.
Who appoints the judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts?
(a) President, according to his own wishes
(b) President, on the advice of the PM
(c) President on the advice of the PM in consultation with the Chief Justice of India
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) President on the advice of the PM in consultation with the Chief Justice of India
Question 12.
Two features of Indian judicial system are:
(a) Independent Judiciary
(b) Integrated Judiciary
(c) Dependent Judiciary
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 13.
Which of the following institutions can make changes to the existing law of the country?
(a) The Supreme Court
(b) The President
(c) The Prime Minister
(d) The Parliament
Answer: (d) The Parliament
Question 14.
Which body acts as the guardian of Fundamental Rights?
(a) District Courts
(b) Supreme Court
(c) Election Commission
(d) Legislature
Answer: (b) Supreme Court
Question 15.
Why does the political executive have more powers than the permanent executive?
(a) Because hardly any expertise is required in taking policy decisions
(b) Because political executive consists of the direct representatives of the people
(c) Political leaders are more educated
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Because political executive consists of the direct representatives of the people
Question 16.
Whom does the President appoint as the Prime Minister?
(a) Anyone he likes
(b) Leader of the majority party
(c) MP who has secured the largest number of votes
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Leader of the majority party
Question 17.
What is the government formed by an alliance of two or more political parties called?
(a) Cooperation government
(b) Coalition government
(c) Consensus government
(d) Cooperative government
Answer: (b) Coalition government
Question 18.
Which of these options is/are correct regarding the powers of the Prime Minister?
(a) He chairs the Cabinet meetings
(b) He distributes work to the different departments
(c) He can dismiss ministers
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 19.
Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) The Judiciary safeguards the laws
(b) The Legislature implements the laws
(c) The political executives are more powerful than the permanent executives
(d) The permanent executives comprises the civil servants
Answer: (b) The Legislature implements the laws
Question 20.
The president of India is elected by
(a) Direct Election by citizens … 18 years of age
(b) Indirect Election by the Electoral College
(c) The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Indirect Election by the Electoral College
Question 21.
The judges of Supreme Court are appointed by
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Chief Justice
(d) Law Minister
Answer: (a) President
very short questions.....
Question 1.
Name the three organs of the Government.
Answer:
Question 2.
Who is the head of the state and the head of the government?
Answer:
The President is the head of the state whereas Prime Minister is the head of the government.
Question 3.
What is a Parliament? Name the two houses of the Parliament.
Answer:
It is the supreme law making body of India. It has two Houses :
Question 4.
What are institutions?
Answer:
The arrangements which are made in modern democracies to run the government.
Question 5.
Name any three institutions responsible to run the democratic government in India.
Answer:
Question 6.
Name the institution where disputes between citizens and the government are finally settled.
Answer:
The Supreme Court.
Question 7.
Why democratic governments insist on institutions? Give two reasons.
Answer:
Question 8.
Which House has more power regarding the money bill? Give reason.
Answer:
The Lok Sabha exercises more powers in money matters. Once the Lok Sabha passes the budget of any other money related law, the Rajya Sabha cannot reject it. The Rajya Sabha can only delay it by 14 days or suggest changes, in it. The Lok Sabha may or may not accept these changes.
Question 9.
Explain No Confidence Motion.
Answer:
Only a person who enjoys the support of the majority of the members of the Lok Sabha is appointed as the Prime Minister. If a no confidence motion is moved in the Lok Sabha, and passed, then,the Government has to resign.
Question 10.
With reference to the Rajya Sabha answer the following questions:
(i) What is its power relating to money bill?
(ii) Can it pass a No-Confidence Motion?
Answer:
(i) A Money bill can originate only in the Lok Sabha. When it is sent to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot reject it. The Rajya Sabha can delay it for 14 days.
(ii) No, Rajya Sabha cannot pass the No-confidence Motion.
Question 11.
Define Executive. [CBSE 2015]
Answer:
At different levels of any government we find functionaries who take day-to-day decisions, but do not exercise the supreme power on behalf of the people. All those functionaries are collectively known as the executive.
Question 12.
Who appoints the Prime Minister?
Answer:
The Prime Minister is appointed by the President.
Question 13.
What is the tenure of the Prime Minister?
Answer:
The Prime Minister does not have a fixed tenure. Normally a Prime Minister is elected for 5 years, but remains in power till he enjoys the majority support.
Question 14.
Who are Cabinet Ministers?[CBSE 2013, 14]
Answer:
They are usually the top level leaders of the ruling party or parties, who are in charge of the major ministries like Defence, Railway, Foreign Affairs etc. Normally, all the major decisions are taken by these ministers.
Question 15.
What is judiciary? [CBSE 2015]
Answer:
All the courts at different levels in a country are called the judiciary.
Question 16.
Which is the highest court of India?
Answer:
The Supreme Court.
Question 17.
“The Constitution of India has made necessary provisions for ensuring independence of judiciary.” Justify your answer by giving two reasons.
Answer:
Question 18.
Who appoints the Chief Justice of India and the other judges?
Answer:
The President of India appoints the Chief Justice of India. The President consults other Judges of the Supreme Court and the High Courts while making appointments of other judges.
Question 19.
State any two powers of the Supreme Court of India.
Answer:
Question 20.
What is the composition of Indian judiciary?
Answer:
Question 1.
Why is there a need for political institutions? [CBSE 2014,15]
Answer:
Question 2.
Distinguish between political executive and permanent executive.
Answer: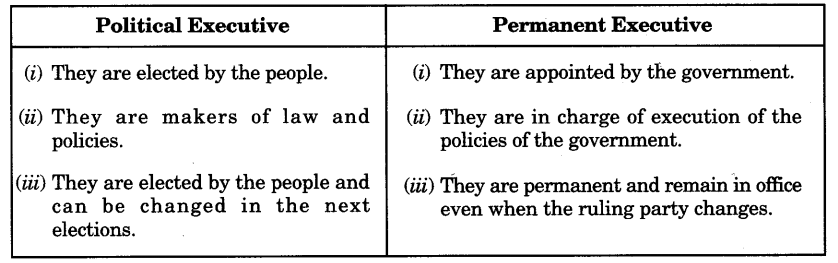
Question 13.
Compare the power, tenure and working of both the Houses of the Indian Parliament. [CBSE March 2011]
Or
The Lok Sabha is more powerful than the Rajya Sabha. Explain by giving three reasons. [CBSE March 2012,13]
Or
Which house of the Parliament is more powerful in India? Give reasons.[CBSE March 2011,2012]
Or
Our Constitution does give the Rsgya Sabha some special powers over the states, but Lok Sabha exercises supreme power. How? Explain. [CBSE March 2012]
Answer: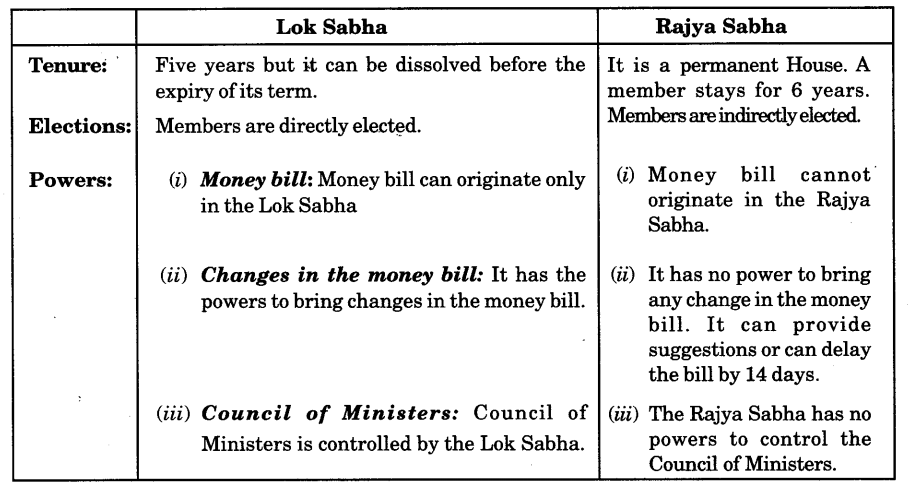
Question 4.
Why do the political executives have more power than the permanent executives? [CBSE March 2014]
Answer:
Question 1.
Explain the major powers and functions of the Prime Minister.
Answer:
Question 2.
Explain the major powers and functions of the Parliament.
Answer:
Question 3.
Explain briefly the powers and functions of the Supreme Court.
Answer:
Question 1.
Explain the composition of the Council of Ministers.[CBSE March 2011,12,13,15]
Or
What is meant by council of Ministers? Explain the different categories of ministers.[CBSE March 2013]
Answer:
The Council of Ministers is a large body, it consists all the three ranks of ministers. The Council of Ministers comprises of the three categories of ministers. These are:
Question 2.
Give any three functions (or responsibilities) of the government.[CBSE March 2011,12,13]
Answer:
Question 3.
What is public interest litigation? What is its importance?[CBSE March 2011]
Answer:
Any one can approach the courts if public interest is hurt by the actions of government. This is called the public interest litigation. The courts intervene to prevent the misuse of the government’s power to make decisions. They check the malpractices on the part of public officials.
Question 4.
What is job reservation? What is its importance?
Answer:
Under job reservation policy some percentage of total government job vacancies are reserved for people and communities who are economically or socially backward. Job reservation policy give a fair opportunity to those communities who so far had not adequately been represented in government employment.
Why is there a need for political institutions? [CBSE 2015]
Or
Why are political institutions important? Give any three points.[CBSE March 2011]
Answer:
Comments
Post a Comment